Dermatitis Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- 3 September 2022
Dermatitis is a medical condition that involves inflammation of the skin. It is a common skin disorder that affects people of all ages. Dermatitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and immune system disorders. It can be acute or chronic, and the symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. In this article, we will discuss the different types of dermatitis, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Types of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis, and each type has different causes and symptoms. The most common types of dermatitis include:
- Atopic dermatitis: This is a chronic form of dermatitis that is often hereditary. It is commonly referred to as eczema, and it is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin.
- Contact dermatitis: This type of dermatitis is caused by contact with an irritant or allergen. It is characterized by red, itchy, and swollen skin that may blister or crack.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This type of dermatitis affects the scalp, face, and chest. It is characterized by scaly, red patches of skin that may itch.
- Nummular dermatitis: This is a type of dermatitis that is characterized by round, coin-shaped patches of inflamed skin.
Causes of Dermatitis
The causes of dermatitis can vary depending on the type of dermatitis. Some of the common causes include:
- Genetics: Atopic dermatitis is often hereditary, and it can be passed down from parents to children.
- Environmental factors: Contact dermatitis can be caused by exposure to irritants or allergens in the environment, such as soaps, detergents, or certain metals.
- Immune system disorders: Some types of dermatitis, such as atopic dermatitis, are caused by immune system disorders that affect the skin.
- Stress: Stress can also trigger or exacerbate dermatitis symptoms.
Symptoms of Dermatitis
The symptoms of dermatitis can vary depending on the type of dermatitis. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Redness: The affected area of skin may appear red and inflamed.
- Itching: Dermatitis is often accompanied by itching, which can be severe in some cases.
- Scaling: Some types of dermatitis, such as seborrheic dermatitis, can cause scaly patches of skin.
- Blisters: Contact dermatitis can cause blisters to form on the skin.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis
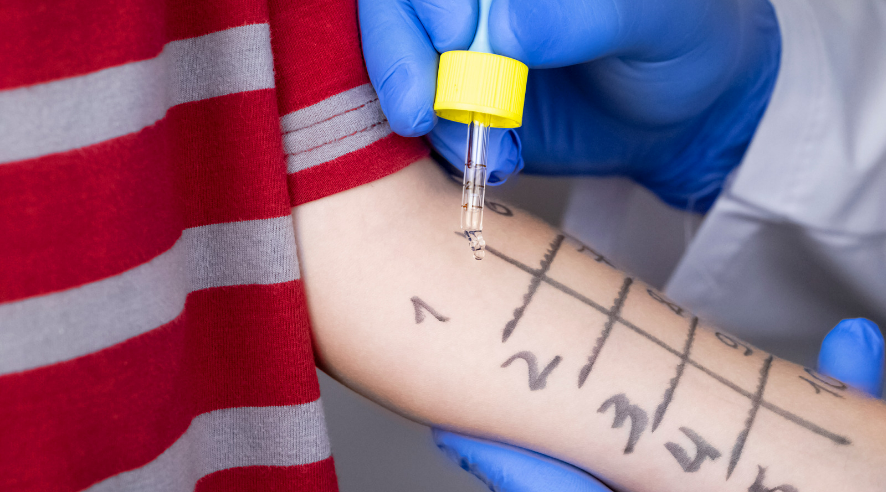
The diagnosis of dermatitis is usually based on a physical examination of the affected area of skin. The doctor will look for signs of inflammation, such as redness and swelling. They may also ask about any recent exposure to irritants or allergens. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Dermatitis
The treatment of dermatitis depends on the type and severity of the condition. In some cases, no treatment is necessary as the symptoms will resolve on their own. However, in more severe cases, treatment may be required. Let's take a look at some of the most common treatment options for dermatitis.
The treatment of dermatitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some of the common treatment options include:
Topical corticosteroids: These are creams or ointments that are applied directly to the affected area of skin. They can help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: These are medications that can help relieve itching and reduce allergic reactions.
- Moisturizers: These can help soothe dry, itchy skin and prevent further irritation.
- Avoidance of irritants or allergens: If the dermatitis is caused by exposure to an irritant or allergen, it may be necessary to avoid these substances.
- Light therapy: This involves exposing the affected area of skin to certain wavelengths of light.
- Immunosuppressants: In severe cases of dermatitis, such as severe atopic dermatitis, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, which can help reduce the severity of symptoms. However, they can also have serious side effects, and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Wet dressings: Wet dressings can be applied to the affected area of skin to help soothe itching and reduce inflammation. They involve applying a wet dressing to the skin and then covering it with a dry bandage or wrap. This can help moisturize the skin and reduce itching.
- Behavioral therapy: Some people with dermatitis may benefit from behavioral therapy, which can help them learn coping strategies for managing stress and anxiety. Stress and anxiety can trigger or exacerbate symptoms of dermatitis, so learning to manage these emotions can be an important part of treatment.
Prevention of Dermatitis
There are several steps you can take to help prevent dermatitis. Some of the common prevention strategies include:
- Avoiding irritants and allergens: If you know that you are allergic or sensitive to certain substances, such as certain types of soaps or metals, avoid them as much as possible.
- Moisturizing: Regularly moisturizing your skin can help prevent dryness and reduce the risk of developing dermatitis.
- Wearing protective clothing: If you work with chemicals or other irritants, wear protective clothing, such as gloves or long-sleeved shirts.
- Managing stress: Stress can trigger or exacerbate symptoms of dermatitis, so learning to manage stress can be an important part of prevention.
Conclusion
Dermatitis is a common skin disorder that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and immune system disorders. It can be acute or chronic, and the symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, moisturizers, and avoidance of irritants or allergens. In severe cases, immunosuppressants or wet dressings may be prescribed. Prevention strategies include avoiding irritants and allergens, moisturizing, wearing protective clothing, and managing stress. If you suspect that you may have dermatitis, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.